Technical Services Area
Publish Date:2017-05-31
Migration Area
There are two types of migration; electronic records format migration and media migration. Electronic records format migration refers to the use of PEARS (Preserving Electronic Archives & Records Suite) or Shared Component Library to migrate electronic records of different formats into compliant formats specified in Addendum 8 of "The Regulation". Media migration refers to copying data stored from old media onto new media, and encapsulate and signify using the certificates issued by government institutions (or certificates issued from the server software), while ensuing the integrity and usability of the replicated data.
PEARS currently incorporates the multimedia preservation technology developed by National Taipei University of Technology (migrating from MPEG-2 to H.264, and from GIF to PNG), and features a proprietary Shared Component Library. The scope of electronic record migration currently includes TIFF to JPEG, JPEG to TIFF, TIFF to PNG, WDL to PDF/A, DOC to PDF/A, WMV to MPEG-2, DOCX to PDF/A, POSTSCRIPT to PDF/A, DOC to ODT, PPT to PDF/A, XLS to PDF/A, EML to PDF/A, MP3 to WAV, TIFF to PDF/A, and electronic record encapsulation. Other migration tools such as PDFCreator (outputs TIFF, JPGE, PDF and PDF/A formats), GhostScript (outputs PDF and PDF/A formats), FFmpeg (outputs MPEG-2 and H.264 formats), and OpenOffice (outputs ODT format) have also been developed.
Media migration currently allows VHS/Beta/Betacam to DVD, CD to DVD, Vinyl/Tape/floppy disk to DVD, microfilm to DVD (JPEG/TIFF/PDF formats) etc; other methods of media migration are currently being developed.
All forms of migration are prone to the risk of data losses; as a result, there needs to be a verification and validation mechanism in place to ensure the quality of migrated data.
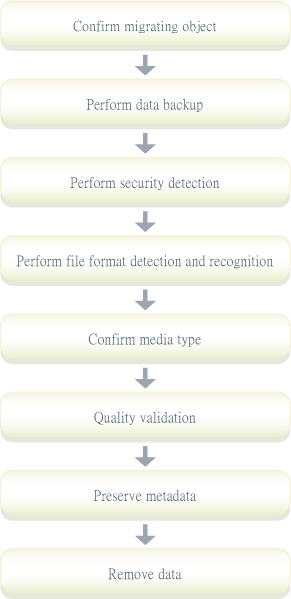
Migrating procedure
Recovery Area
Electronic records may require recovery if they cannot be opened or encounter errors of some sort.
1.Recovery of storage media: Refers to the situation when the storage media containing the electronic records has been or is about to be damaged, to the extent that data is only accessible by replacing or repairing hardware components.
2. Content recovery: The possibility that only partial contents may be recovered.
3. File recovery: Refers to the situation that the electronic record becomes inaccessible due to incorrect directory location, and needs to be retrieved by scanning or other methods.
Currently, ERTSC is able to recover corrupted electronic records, hard disk data, floppy disk data, and restore disc surface. It is also capable of duplicating data saved on the storage media and ensuring accessibility.
ERTSC utilizes a variety of data recovery tools such as R-Studio and FinalData for recovering files that have been deleted by mistake, PC-3000 for repairing IDE hard drives, disc scratch removers for restoring scratched surfaces, and handheld Forensic Talon (a digital forensics tool) for quick capture and replicate of hard disk data.

Attachments: